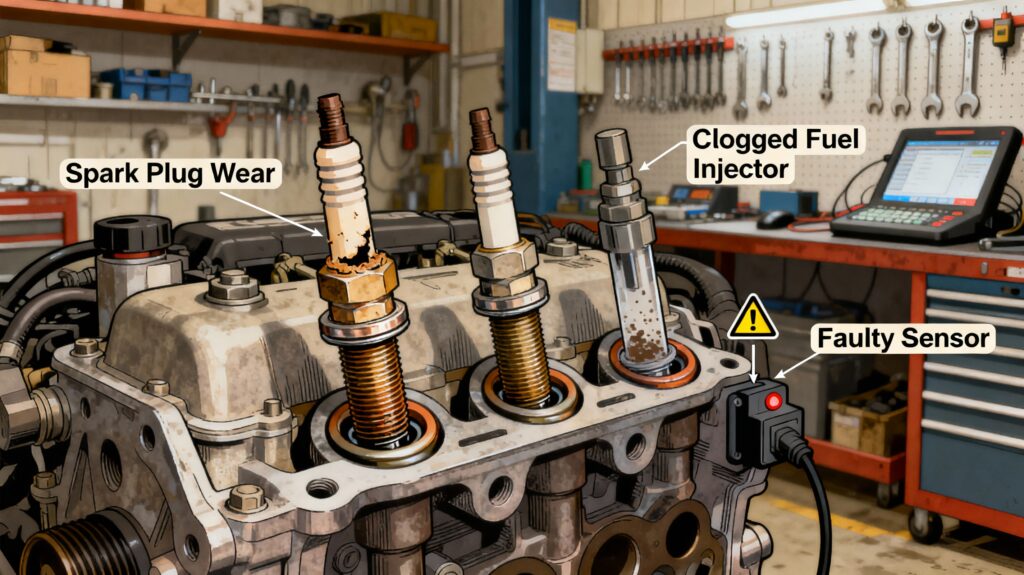
When it comes to maintaining the health and performance of your vehicle, understanding engine cylinder misfires is crucial. These misfires can significantly diminish your car’s efficiency and reliability, leading to poor fuel economy, reduced power output, and even engine damage if not addressed promptly.
A misfire can occur for several reasons, including ignition issues, fuel system inadequacies, and compression problems, all of which can stem from common parts like spark plugs and injector systems.
In this article, we will explore the typical causes of engine cylinder misfires and delve into practical solutions that can help you identify and resolve these issues effectively. By arming yourself with this knowledge, you can enhance your vehicle’s performance and ensure it runs smoothly for years to come.
| Cause | Description | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Ignition Issues | Problems with spark plugs, ignition coils, or wiring can lead to spark failure, causing the cylinder to misfire. | Inspect and replace worn spark plugs or faulty ignition coils. Ensure all wiring is intact. |
| Fuel System Problems | Issues such as clogged fuel injectors or a faulty fuel pressure regulator can disrupt fuel delivery. | Use fuel injector cleaners. Replace clogged injectors and check the fuel pressure regulator. |
| Air and Compression Issues | Low compression due to worn piston rings, valves, or head gaskets can lead to poor air-fuel mixing. | Conduct a compression test. Repair or replace worn components. |
| Sensor/ECU Problems | Faulty sensors (like the oxygen sensor) or issues with the engine control unit (ECU) can mislead the engine’s performance adjustments. | Diagnose and replace faulty sensors. Ensure the ECU is properly calibrated and functioning. |
Ignition Issues as a Cause of Engine Cylinder Misfire
Ignition issues are a significant contributor to engine cylinder misfires, as they disrupt the vital spark needed for the combustion process to occur efficiently. The primary components involved in the ignition system, mainly spark plugs and ignition coils, play a critical role in preventing misfires.
Spark Plugs
Spark plugs are responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. Over time, these components can wear out due to heat, deposits, and carbon buildup, ultimately leading to poor engine performance. A worn spark plug can cause weak or inconsistent sparks, which in turn can result in engine cylinder misfires.
Signs of Worn Spark Plugs:
- Engine hesitation or stumbling
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Increased fuel consumption
- Rough idling
To check spark plugs, you will need to:
- Locate the spark plugs: These are usually found on the top or side of the engine block, connected by ignition wires.
- Inspect visually: Look for signs of wear, such as cracks, carbon buildup, or corrosion.
- Use a spark plug gauge: Check the gap between the electrodes to ensure it meets manufacturer specifications.
If the spark plugs appear damaged or worn beyond use, replacing them is essential. Ensure you tighten them to the specified torque to avoid any issues after installation.
Ignition Coils
Ignition coils function to amplify the voltage from the battery to create a sufficient spark at the spark plugs. If an ignition coil is faulty, it might not deliver the necessary voltage, also leading to engine cylinder misfires.
Signs of Faulty Ignition Coils:
- Engine warning light on the dashboard
- Misfiring or rough acceleration
- Poor fuel economy
To check ignition coils:
- Locate the coils: Typically, they sit on top of the engine and are attached directly to the spark plugs.
- Visually inspect: Look for cracks, signs of overheating, or corrosion at the electrical connections.
- Test the ignition coil: Using a multimeter, testers can measure the resistance in the ignition coil to ensure it is within the specified range.
If you find a faulty ignition coil, replacing it promptly is crucial. Make sure to disconnect the battery before you begin repairs, and again, tighten new coils to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Conclusion
Ensuring your ignition system is in good condition is vital in preventing engine cylinder misfires. Regular inspection and maintenance of spark plugs and ignition coils can lead to smoother engine performance, greater fuel efficiency, and a reduction in long-term repair costs. By addressing these components early on, you can effectively enhance your vehicle’s reliability and overall functionality.
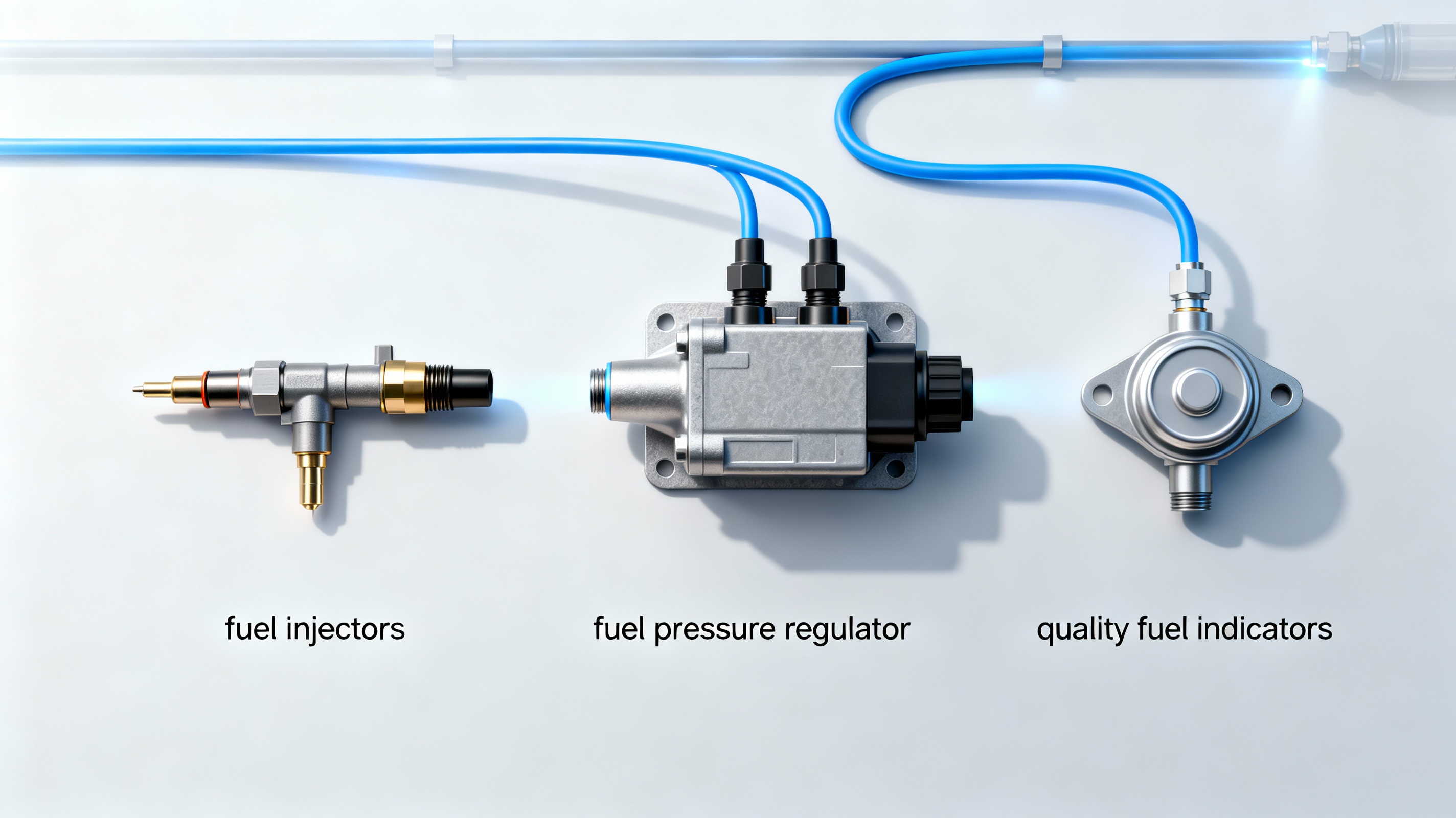
Fuel System Problems That Can Lead to Misfires
The fuel system in a vehicle plays a critical role in ensuring efficient combustion within the engine. Any disruption in the fuel delivery process can lead to engine cylinder misfires. Below, we explore key components such as fuel pressure regulators and injectors and the importance of using quality fuel to maintain vehicle performance.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is tasked with maintaining the correct fuel pressure within the fuel system. If it fails to regulate the mixture properly, it may lead to misfires, as the engine may receive too much or too little fuel.
Symptoms of a Faulty Fuel Pressure Regulator:
- Poor acceleration
- Increased fuel consumption
- Fuel leaks under the vehicle
Marko Mikulic points out, “If your fuel pressure regulator isn’t able to properly regulate the mixture, it may lead to the same problem.” Regular inspection and immediate replacement of a faulty regulator can prevent significant engine issues.
Fuel Injectors
Fuel injectors are responsible for delivering the precise amount of fuel to each cylinder. Clogged or failing injectors can lead to inconsistent fuel flow, causing misfires. Using low-quality fuels can lead to sediment build-up, affecting injector performance.
Signs of Clogged Fuel Injectors:
- Engine hesitation during acceleration
- Rough idle
- Engine knocking sounds
Using dedicated fuel injector cleaners can help maintain injector performance, while regular cleaning or replacement may be necessary if issues persist.
Quality of Fuel
The quality of fuel can significantly affect engine performance. Lower-quality fuels may contain impurities that can clog injectors or disrupt proper combustion. Ensuring the use of high-quality fuel can help prevent premature wear on fuel system components and enhance overall engine efficiency.
As noted in the article from Jalopnik, maintaining quality fuel and regular vehicle maintenance can help prevent misfires, which ultimately leads to a smoother-running engine and better fuel economy.

Air and Compression Issues Affecting Engine Performance
Air and compression issues play a critical role in the overall performance of a vehicle’s engine. The timing chain and compression stroke are two elements closely interlinked, and problems in either can lead to significant loss of power, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased emissions. Understanding these components is vital for effective diagnosis and remediation.
Timing Chain Problems
The timing chain is responsible for synchronizing the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft, which ensures that the engine’s valves open and close at the correct times. If the timing chain becomes stretched or worn, it may cause poor engine performance, such as:
- Engine misfires
- Rough idling
- Reduced engine power
- Stalling
When the timing chain is not functioning properly, it can lead to inaccurate valve timing, causing loss of compression. Diagnosis of a timing chain issue may involve:
- Listening for metallic rattling noises from the engine
- Checking engine codes, such as P0340, indicating camshaft position sensor issues
- Using a timing light to verify the timing
To resolve timing chain problems, one may need to:
- Replace the timing chain and tensioners
- Ensure proper alignment during installation to prevent future issues.
For more detailed information, you can check out this Car and Driver article on timing chain problems.
Compression Stroke Issues
The compression stroke is a crucial phase in the four-stroke engine cycle. During this phase, the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture before ignition. Low compression due to worn piston rings, leaking valves, or head gasket failure can significantly decrease engine power and efficiency.
Symptoms of low compression include:
- Engine misfires
- Reduced power during acceleration
- Increased fuel consumption
To diagnose compression-related issues, methods include:
- Performing a compression test
- Conducting leak-down tests
- Inspecting the engine with a borescope
Solutions for addressing compression problems typically involve:
- Replacing worn piston rings
- Repairing or replacing valves
- Fixing head gaskets
In addition, issues with the timing chain may indirectly affect compression by causing valves to open or close at incorrect times. A stretched chain can lead to late valve closings, thereby allowing the compressed air-fuel mixture to escape, which reduces cylinder pressure. As such, when compression tests reveal low readings, it is essential to check both compression and timing aspects for a complete diagnosis. For further insights, view this detailed resource on the interplay between timing chain and engine compression at AutoZone.
Conclusion
Proper maintenance and regular inspection of both the timing chain and the compression system are crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance. By diagnosing these problems early and taking appropriate corrective actions, vehicle owners can enhance efficiency, extend engine life, and prevent costly repairs down the road.
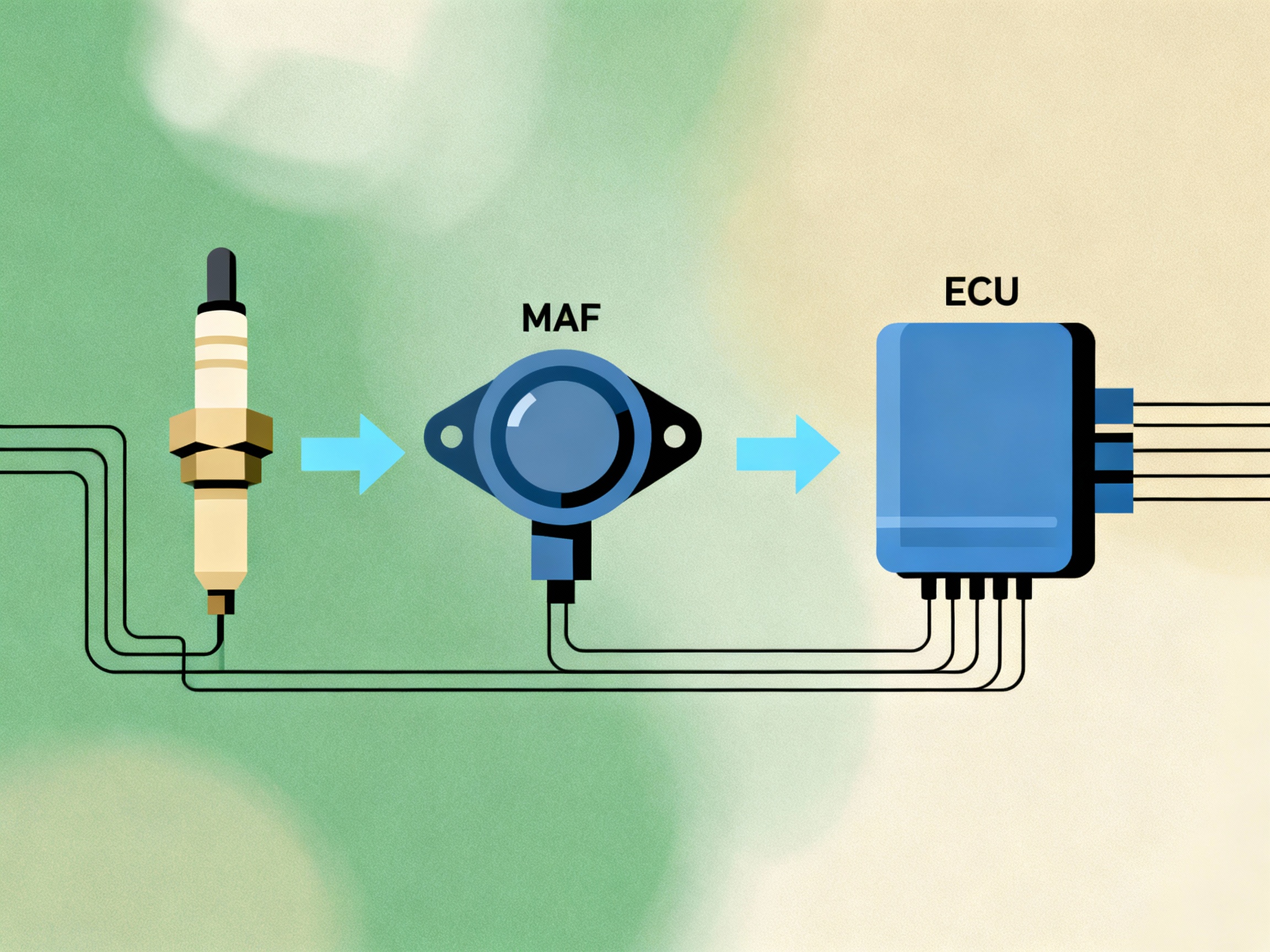
Sensor and ECU Problems Leading to Engine Misfires
Sensor and ECU (Engine Control Unit) malfunctions can cause significant engine performance issues, particularly leading to engine cylinder misfires. These misfires may manifest as rough idling, stalling, or hesitation during acceleration, severely impacting a vehicle’s efficiency and safety.
The Role of Sensors
- Oxygen Sensors: These sensors monitor the level of oxygen in the exhaust gases and send this data to the ECU. If the sensor fails, it can send incorrect information, resulting in a misadjusted air-fuel mixture that can either be too rich or too lean, leading to engine misfires. According to YourMechanic, symptoms of a failing oxygen sensor include rough idling and misfires under load. Testing sensor voltage output and replacing sensors every 60,000 to 90,000 miles is recommended for preventive maintenance.
- Mass Airflow Sensors (MAF): These sensors measure the amount of air entering the engine, allowing the ECU to gauge how much fuel is needed for optimal combustion. Issues with the MAF can disrupt this balance, leading to misfires.
- Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Sensors: These sensors help to determine the position of the crankshaft and camshaft to optimize ignition timing and fuel injection. Faulty readings from these sensors can alter engine timing, causing misfires.
The Importance of Electrical Connections
Maintaining good electrical connections to the sensors and ECU is crucial. Issues such as fraying wires, corroded connectors, or loose terminals can disrupt the signals sent to and from the ECU, leading to erratic engine behavior. As noted in FIXD, securing and inspecting wiring harnesses, ensuring connectors are fully seated, and using dielectric grease can prevent moisture ingress, reducing the risk of misfires.
Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some actionable tips for diagnosing sensor and ECU-related issues:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly check for damaged wiring and connectors. Look for signs of wear or corrosion.
- Error Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for error codes that might indicate specific sensor failures or ECU issues. This can pinpoint which component needs attention.
- Voltage Testing: Using a multimeter, test the voltage outputs of various sensors to ensure they are within the manufacturer’s specified range. This can help in identifying any faulty sensors before they lead to misfires.
- Connector Maintenance: Clean sensor connectors and apply anti-corrosion compounds as needed. Regular maintenance can help avoid malfunctions by ensuring good electrical contact.
- Replace Faulty Sensors: If any sensors are identified as faulty, replace them promptly. As suggested by AutoZone, replacing oxygen sensors and ensuring all sensors are in optimal working condition can prevent misfires.
Conclusion
To maintain vehicle performance and prevent misfires, regular inspections and cleaning of sensors and ensuring electrical connections are secure is key. By taking proactive steps to address these components, you can considerably enhance engine performance, fuel economy, and overall driving satisfaction.
In conclusion, understanding the challenges posed by engine cylinder misfires is vital for every vehicle owner. Identifying the common causes—such as ignition anomalies, fuel delivery disruptions, air and compression issues, and sensor failures—equips drivers with the knowledge needed to act promptly.
Regular maintenance practices, including periodic inspections, maintaining quality fuel, and using dedicated cleaning products, significantly contribute to preventing misfires. Timely diagnosis not only enhances engine efficiency but also preserves the longevity of the vehicle, ultimately leading to a smoother driving experience and cost savings on repairs.
By prioritizing these steps, vehicle owners can ensure they keep their engines running optimally, safeguarding against the consequences of negligence.
Understanding Vehicle Owner Awareness of Engine Cylinder Misfires
Research indicates a significant lack of awareness among vehicle owners regarding engine cylinder misfires and their potential impacts on vehicle performance. An analysis of complaints revealed that in 2025, complaints related to misfires increased by 18%, particularly highlighting issues with three-cylinder engines. Alarmingly, 80% of reported faults were linked to ignition system failures, fuel delivery problems, and electrical circuit issues, indicating that many drivers may not recognize the symptoms of misfires or their serious implications for vehicle health.
A separate analysis emphasizes that neglecting the symptoms of engine misfires can lead to a 20-30% increase in fuel consumption, alongside heightened emissions levels and potential risk of engine damage—such as catalytic converter failure. The need for awareness is clear, as many vehicle owners may overlook crucial maintenance signs, ultimately affecting both the longevity of their vehicles and their operational efficiency.
This lack of understanding underlines the importance of education on engine maintenance, specifically regarding the identification and implications of misfires. By empowering drivers with knowledge about these issues, they can engage in proactive maintenance that preserves not only vehicle performance but also safety on the road.